AICorr dives into the world of machines, exploring the integration of AI in robotics.
Table of Contents:
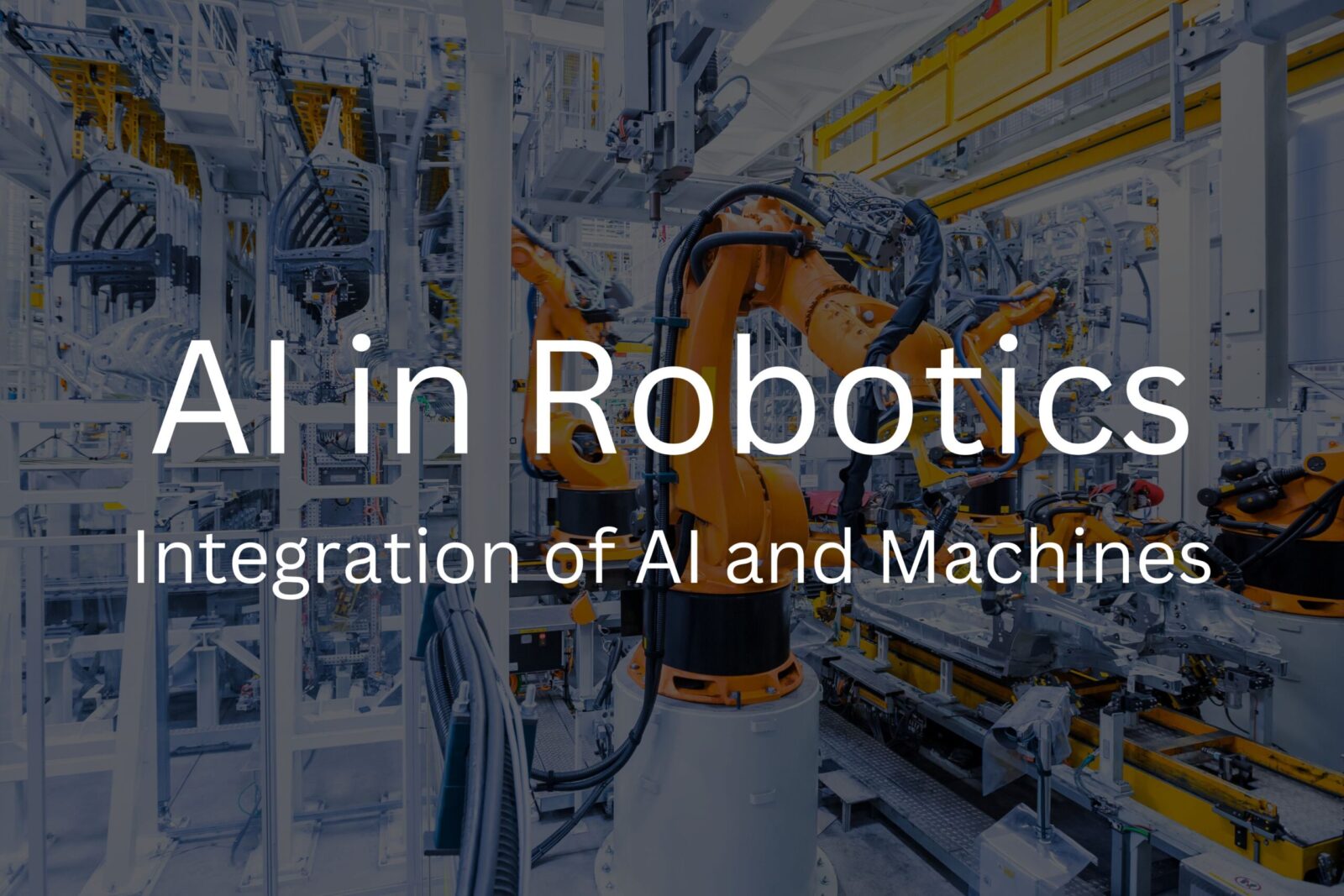
AI in Robotics
Robotics, in the context of artificial intelligence (AI), involves the development and integration of machines. Machines that are capable of interacting with the physical world in ways that mimic or exceed human capabilities. AI enhances robotic systems by enabling them to make decisions. In addition, learn from experience, and adapt to new environments without direct human input.
The evolution of robotics has seen a profound shift with the integration of artificial intelligence (AI). Transforming machines from simple mechanical devices to sophisticated systems. As such, capable of interacting with the physical world in a dynamic, intelligent manner. AI enhances the abilities of robots by allowing them to perceive, learn, adapt, and make autonomous decisions. This fusion has led to innovations in a wide range of industries. From manufacturing and healthcare to autonomous vehicles and space exploration, fundamentally altering how we engage with machines.
The Role of Perception in AI-Powered Robots
One of the most critical aspects of AI in robotics is the ability for machines to perceive their environment. Traditional robots operate based on pre-programmed instructions, relying on a fixed set of rules to perform specific tasks. However, AI gives robots the capability to sense and interpret real-time data from the world around them, significantly broadening their functionality. This is achieved through the use of sensors such as cameras, LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), ultrasonic sensors, and more.
For example, self-driving cars, a widely recognised application of AI and robotics, use a combination of cameras, radar, and LIDAR. They gather information about their surroundings, from detecting obstacles and road signs to recognising other vehicles and pedestrians. AI algorithms then process this data, allowing the vehicle to make decisions about accelerating, braking, or steering without human intervention. This same principle applies to drones used for surveying or delivery, as well as industrial robots tasked with identifying defects in manufacturing processes.
Learning and Adaptation: A New Era of Robotic Intelligence
AI empowers robots not just to follow orders but to learn and adapt over time. This learning process is typically achieved through machine learning. ML is a subset of AI where algorithms learn from data and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed for each task. This capability is particularly transformative in environments where the robot must deal with variability or unexpected changes.
For instance, in industrial settings, robots traditionally needed to be reprogrammed whenever there was a change in the production line. With AI, modern robots can learn to adapt to these changes autonomously, adjusting their behavior based on new input. A robot arm, for example, may use machine learning to perfect its movements over time. Hence, improving efficiency and reducing waste in the assembly process.
In healthcare, surgical robots equipped with AI can analyse data from previous procedures. In order to refine their precision and improve outcomes in real-time. This level of adaptability allows robots to perform increasingly complex tasks that previously required a human operator. Therefore, making surgery safer and more efficient.
Autonomous Decision Making: AI Enables True Robot Autonomy
One of the ultimate goals of integrating AI into robotics is to grant machines the ability to make decisions autonomously. AI algorithms, particularly those based on reinforcement learning, allow robots to evaluate different actions and choose the most appropriate one based on the situation at hand. This capability is vital in environments where quick decision-making is essential. Or where human intervention is not feasible, such as in disaster zones, underwater exploration, or space missions.
Consider the Mars rovers operated by NASA, such as Perseverance. These rovers are equipped with AI systems that allow them to navigate the Martian surface autonomously. Given the long communication delays between Earth and Mars, it would be impractical for human operators to control every movement in real-time. Instead, the rover’s AI processes information about the terrain, obstacles, and scientific objectives, making decisions on how to proceed.
Similarly, in warehouse automation, robots like those developed by Amazon use AI to navigate the facility. In addition, picking and transporting items based on real-time inventory data. These robots can manage tasks without constant human oversight, dramatically increasing operational efficiency.
Manipulation and Interaction: AI Brings Robots Closer to Human-Like Abilities
Another significant area of AI integration in robotics is the enhancement of manipulation and physical interaction capabilities. AI allows robots to perform tasks requiring dexterity, precision, and feedback-based adjustment. As such, bringing them closer to human-like interaction with the world. This is particularly important in fields like healthcare, manufacturing, and service industries.
Robotic arms used in assembly lines, for example, have been traditionally limited to repetitive, pre-programmed motions. However, with AI, these robots can now adjust their movements in real-time. And as such, responding to variables like the placement of an object or slight changes in its dimensions. This precision is also crucial for surgical robots. Where tiny adjustments in movement can make the difference between a successful operation and complications.
In the service industry, robots equipped with AI can interact with humans more naturally. Social robots, such as those used in elder care or customer service, use AI to interpret speech, facial expressions, and body language. As such, allowing them to respond appropriately. This capability improves the user experience. But also opens the door for robots to take on roles that require a degree of empathy and human-like interaction.
Collaboration with Humans: The Rise of Cobots
The integration of AI into robotics has also given rise to a new class of machines known as collaborative robots, or “cobots.” These robots are designed to work alongside humans, assisting in tasks that require teamwork between human intelligence and robotic precision. Cobots are widely used in manufacturing and other industries where tasks require both flexibility and accuracy.
For example, in automotive manufacturing, cobots assist workers by handling heavy or dangerous materials while humans perform more complex tasks. AI allows these robots to operate safely in close proximity to humans. By adjusting their speed and movements in real-time to avoid accidents. This combination of human creativity and robotic precision increases productivity and safety.